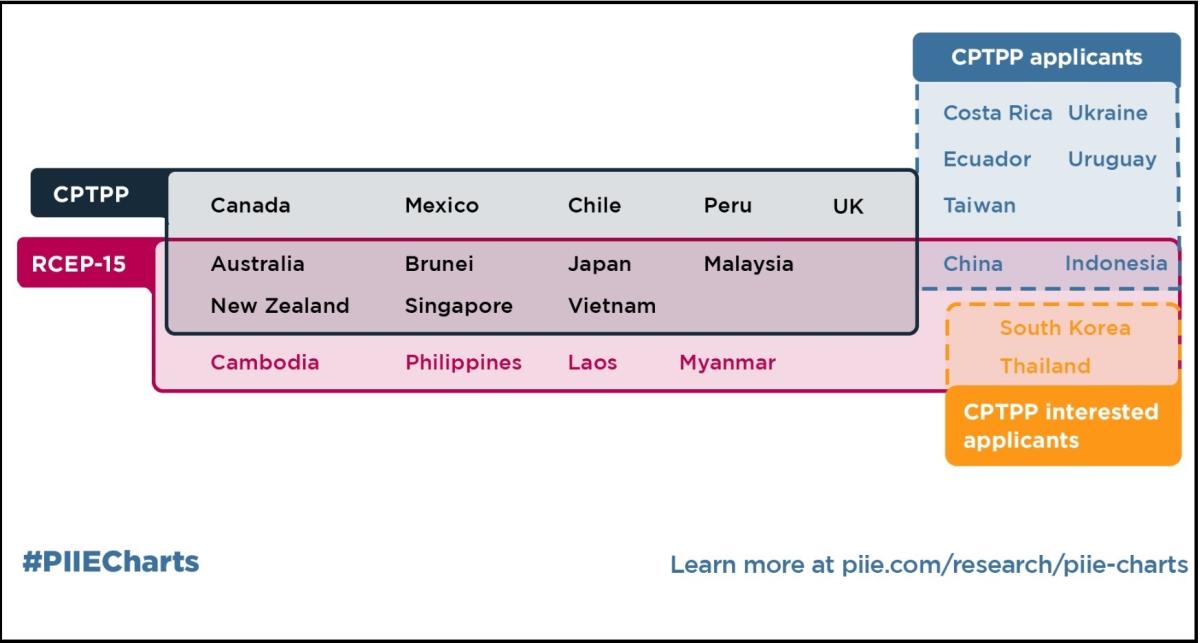
The United Kingdom is the first economy to join the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) through the lengthy accession process that it has established for new members. Members have pledged to eliminate almost all tariffs and import charges on each other's products over time. They have accepted common obligations on food regulations, environmental protections, the digital economy, and regulations governing investment, labor, financial services, and other sectors.
Since taking effect in December 2018, several additional countries have applied or shown interest in joining the CPTPP. Seven CPTPP signatories are also members of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) that took effect in January 2022. RCEP is the world's largest free trade agreement (FTA), encompassing 15 countries that account for 29 percent of 2022 global GDP.
These agreements confront US policymakers with some difficult choices: stay out of the Asia-Pacific megadeals and face increasing trade discrimination in important and growing markets while China deepens its trade and investment ties in the region, or reengage with CPTPP countries and/or develop new and more narrowly focused trade accords with key allies in the region in areas such as digital trade and trade-related climate issues.
You can access the article here.